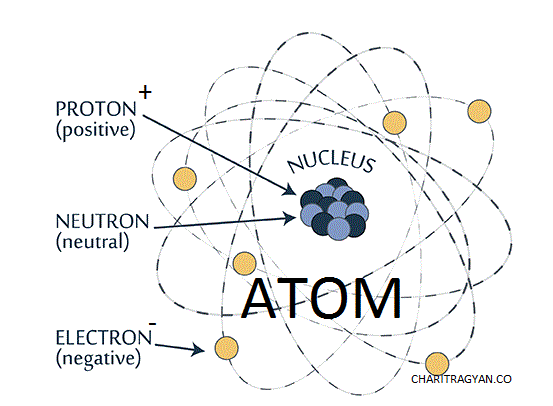
ATOM :
The smallest particle possible in the substance or element which does not exit in free state , but take part in chemical reactions and all characteries of the substance or element are present in it is called the atom.
The world atom in greek means indivisible . The founder of atomic theory John Dalton postulated his theory as.
- Matter is composed of atoms which cannot be subdivide.
- Atom is the smallest particle of matter that takes part in a chemical reaction,
- Atoms of the same element have similar properties like mass, volume and chemical reactivity.
- Atoms combine in definite proportion to from molecules.
Main Fundamental particles of the atom
- Electron :- This fundamental particle was invented by J.J. Thomsam in 1897 and it is a negatively charged particle which rotates in various orbits around the nucleus. The mass of an electron = 9.1 *10 -31 kg and the charge of an electron = - 1.6 * 10 -19 coulomb .
- Proton : - This fundamental particle was invented by Golds ten in 1919 and it is a positively charged stable particle . The mass of a proton = 1.6 * 10 -27 kg and the charge of a proton = 1.6 * 10-19 coulomb.
- Neutron :- This fundamental particle was invented by Chadwick in 1932 which is a neutral unstable particle . The masses of a proton and neutron are nearly equal. mass of a neutron = 1.6 * 10 -22 kg .
- Mass Number :- The sum of the neutrons and protons is known as mass number . it is denoted by a .
Mass Number = Number of neutron + number of proton A = N + P
Atomic Number :
The number of unit positive charge carried by the nucleus of an atom is termed atomic number.
It is denoted by symbol Z
Atomic Number Z = Number of unit positive charge the nucleus = Number of proton is the uncles P = Number of electrons revolving in orbits E
Z = P = E
Atomic number is written on the lower side of the symbol and the mass number is written on the upper side
where
A=Mass Number
Z = Atomic Number
X = symbol of the element
ISOTOPES :-
Atoms of the same element having same atomic number but different mass Number are called isotopes .
For example : - There are three isotopes of hydrogen having mass number 1 . 2. 3 respectively
and each of them having atomic number equal to 1 . they are represented as 1H , 2 H , 3 H
and named protium , deuterium ,tritium .
- Isotopes of chlorine are written as 17 cl and 17 cl
- Isobars :-Such atoms of different elements charging different atomic number but same mass numbers are called isobars . They have different properties .
for example : 18 Ar 40 19 k 40 20 ca 40
- Isotones :- Such atoms of different elementary which contain the same number of neutrons are called isotones . They have different properties .
for example : 6 c 14 7 n 15 8 o 16
- Isoelectronic :- The species atom or ions containing the same number of electrons are called isoelectronic .
for example : O -2 , F - , Na + , Mg +2 , Al +3
Bohrs Model of an Atom ;
Neil's Bohrs 1913 combined some postulates of classical physics and some postulates of the planks quantum theory .
The important postulates of Bohr's models of an atoms
- Electrons are continuously revolving around the nucleus in a certain circular path know as orbit shells / energy levels. These orbit are stationary these shells are denoted as 1,2,3,4,......Electrons move in these orbits of fired energy called stationary state.
- The coulombic force of attraction between the nucleus and the electron holds the atom together .
- As long as electron remains in a particular orbit, it does not lose or gain energy , it means if energy remains constant . so these orbits are stationary state .
- Only those orbits are permitted in which the angular momentum of an electron is an integral multiple of h/ 2 . Where is the plank's constant this is known as principle of quantization of energy according to which .
- The energy is absorbed or emitted only when the electrons jump from one energy level to another . this is given by the expression.
successes of Bohrs model
- Bohrs model could explain the stability of an atom :- According to Borhs model an electron revolving in a particular orbit cannot lose energy . The electron can lose energy only if it jumps to some lower energy level . if no lower energy level is vacant then electron will keep in reveling in the same orbit without losing energy .
- Borhs theory helped in calculating energy of an electron in a particular orbit of hydrogen :- on the basis of various postulates of Bohrs model . it is possible to derive a mathematical relation for energy of an electron in nth orbit of hydrogen .
Borhs model could explain the atomic spectrum of hydrogen :- if E1 & E2 are the energies of lower and higher energy levels respectively , them frequency of the radiation emitted is given by the following relation.
Quantum Number :-
A set of four numbers used to specify energy , size, shape , orientation of the electron are called quantum number.
Quantum Numbers are of four types
- Principal Quantum Number N
- Azimuthal Quantum Number L
- Magnetic Quantum Number M
- Spin Quantum Number S
Principle Quantum Number:-
It is denoted by N , It have whole number values starting from 1 to 23......... , The value of n denotes the shell in which an electron is present. the shell with n=1 is called first shell and is denoted by K , Similarly , We have other shell like L,M, N, etc..
N also determines the distance of the electron in a shell when n=1 , electron is closed to the nucleus as the value of n increase , electron gets father away from the nucleus and thus size increase .
N also determines the energy of the electron in given orbit.
N also given maximum number of electron that a shell can accommodate . A shell with principle Quantum number N can contain 2n2 electron.
maximum number of electron in k shell 2 .
maximum number of electron in L shell =8.
maximum number of electron in M shell 18
Azimuthal Quantum Number :-
It is denoted by L
It is related to sub shell s , p , d & f .
I can have all positive whole number values from zero to etc...
L value enable us to calculate the total number of subs shell a main shell has given below .
shell principal q n values of L subshell total number of sub shell
K 1 0 S 1
L 2 0 ,1 S , P 2
M 3 0, 1 , 2 S , P , D 3
N 4 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 S , P , D , F 4
Thus this provides information regarding the shape of orbital .
Magnetic Quantum Number :-
It is denoted by M.
It given idea about the orientation of electron under the influence of an applied magnetic field.
The value of L determines the allowed of M m can have values -L to +L though O. In other words given a total of 2l +1 possible values .
Spin Quantum number :-
It is denoted by S .
It can only two values +1/2 , -1/2 . Instead of giving numbers for s=
+1/2 , -1/2 usually designated arrow pointing ^.